Performance Polymers
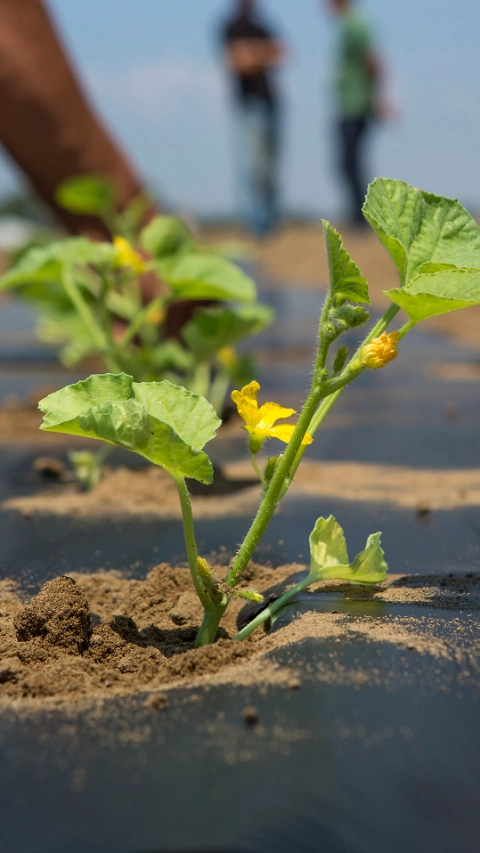
Soil-biodegradable ecovio® for mulch films:
better soil, higher yield and no persistent microplastic
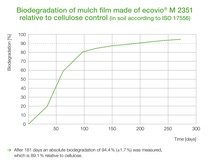
For sustainable agriculture and efficient food production: Certified soil-biodegradable mulch films made of the biopolymer ecovio® M 2351 can remain in the soil and be ploughed in after mechanical harvest. Farmers do not have to laboriously remove and recycle them as with conventional mulch films made of polyethylene (PE), which do not biodegrade. Naturally occurring soil microbes like bacteria or fungi recognize the structure of the film made of ecovio® M as food they can metabolize.
The remaining end products after biodegradation are CO2, water and biomass (mass from natural living organisms, e.g. cells). This results in many benefits for the farmers and for society: Above all, it reduces the amount of persistent microplastics in agricultural soil caused by remains of thin PE mulch films and thus contributes to a sustainable food production that keeps agricultural soil healthy and productive for a longer time.
Benefits of ecovio® M 2351:
- Certified according to the European standard EN 17033
- Increased yield and earlier harvesting
- Less / no herbicides needed
- Less water usage
- Better resistance of plants to fungal diseases
- More homogeneous quality of produce
- Better tasting crop
- Easy, less time-consuming managing of end-of-life
Discover our biopolymers expertise
Sustainability benefit of biopolymers for mulch films: avoids persistent microplastic in agricultural soil

Thin PE mulch films are used by farmers in many countries to increase crop yield. After harvesting it is often impossible for farmers to collect and recycle these films completely, especially when they are only a few micrometers thin. PE residues therefore find their way into the soil and accumulate there, since they do not break down.
Certified soil-biodegradable mulch films made of ecovio® M 2351, which is based on BASF’s ecoflex® (PBAT), can be left in the soil after harvesting, rather than being laboriously removed and recycled.
As maintaining yield stability of agricultural land is of major social importance, extensive internal and external studies have been conducted: They not only verified the soil-biodegradability of mulch films made of ecovio® M 2351, but also identified and analyzed the microbes in the soil (bacteria and fungi) that are involved in biological degradation.
Experience how ecovio® M 2351 proves its worth in agriculture with different crops and climates
Read on: scientific studies on biopolymers for mulch films
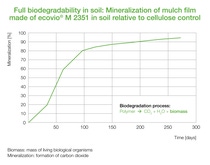
Independent study by ETH Zürich proves for the first time the formation of biomass when PBAT biodegrades in soil
United Nations recognize bioplastics as sustainable alternative to conventional plastics
.jpg)
Now a study from ETH Zürich, Switzerland, has shown for the first time that soil microbes can use films made from the plastic polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) as food.
The microorganisms use the carbon from the polymer both to generate energy and to form biomass. This means that PBAT biologically degrades in the soil and does not remain there as microplastic as PE does.
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) assesses in a report the sustainability of agricultural plastic products and recommends the replacement of non-biodegradable, conventional polymers with biodegradable, bio-based polymers. The study focuses on agricultural plastic products used in different value chains.
A qualitative risk assessment, which accompanies the study, analyses 13 specific agricultural products. The list of recommended products includes among others mulch films as well as plant support twines.
Key advantages of ecovio® M 2351 for mulch film manufacturers
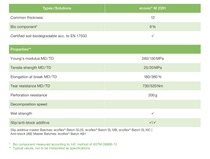
ecovio® M 2351 for mulch consists of BASF’s certified biodegradable co-polyester polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) ecoflex®, other biodegradable polymers made from renewable raw materials and inorganic fillers. Certified soil-biodegradable mulch films made of ecovio® have similar mechanical properties as conventional films and can be employed in the same way.
- Due to its very good mechanical properties, ecovio® M 2351 can be used to make mulch films with layer thicknesses of 12, 10 and 8 μm or 25 μm, if needed.
- ecovio® M 2351 is a ready-to-use compound that can be processed on conventional machines used for the extrusion of polyethylene films without any additional lubricants or anti-block agents.
- With ecovio® M 2351, black mulch films can be manufactured. Compatible masterbatches are available.
Key data
Easy laying-out of soil-biodegradable mulch films made of ecovio® M 2351
Soil-biodegradable mulch films made of the bioplastic ecovio® M 2351 can be laid out with the same machines used for conventional mulch films. Farmers do not have to change the ways in which they work the soil. In order to utilize the excellent mechanical performance of the ecovio® mulch film and thus achieve the best harvesting results, it is important to lay out the mulch film correctly and to prepare the soil accordingly.
Here are the 10 most important rules to observe when using mulch films made of ecovio® M 2351!


Watch the video: This is how ploughing in of mulch films made of ecovio® works.
Excellent performance for many crops and climates

Because of its excellent agronomic performance, mulch films made of ecovio® M 2351 can easily be used in different climates as well as for the cultivation of many fruit and vegetable crops, e.g. tomatoes, cucumber, salad, melons, zucchini and peppers as well as potatoes and rice. Here you find flyers on many crops showing the advantages that mulch films made of ecovio® offer them:
Click for flyers



